The Menzies Director, Professor Alison Venn:
“The first few years of a child’s life lay the foundations for their future,” Professor Venn said.
“The early years have life-long impacts on education, health, job opportunities, and social inclusion.”
“…When children’s pathways through services are known and linked to child outcomes… [they] improve children’s health and wellbeing, education and care before they start full-time school.”
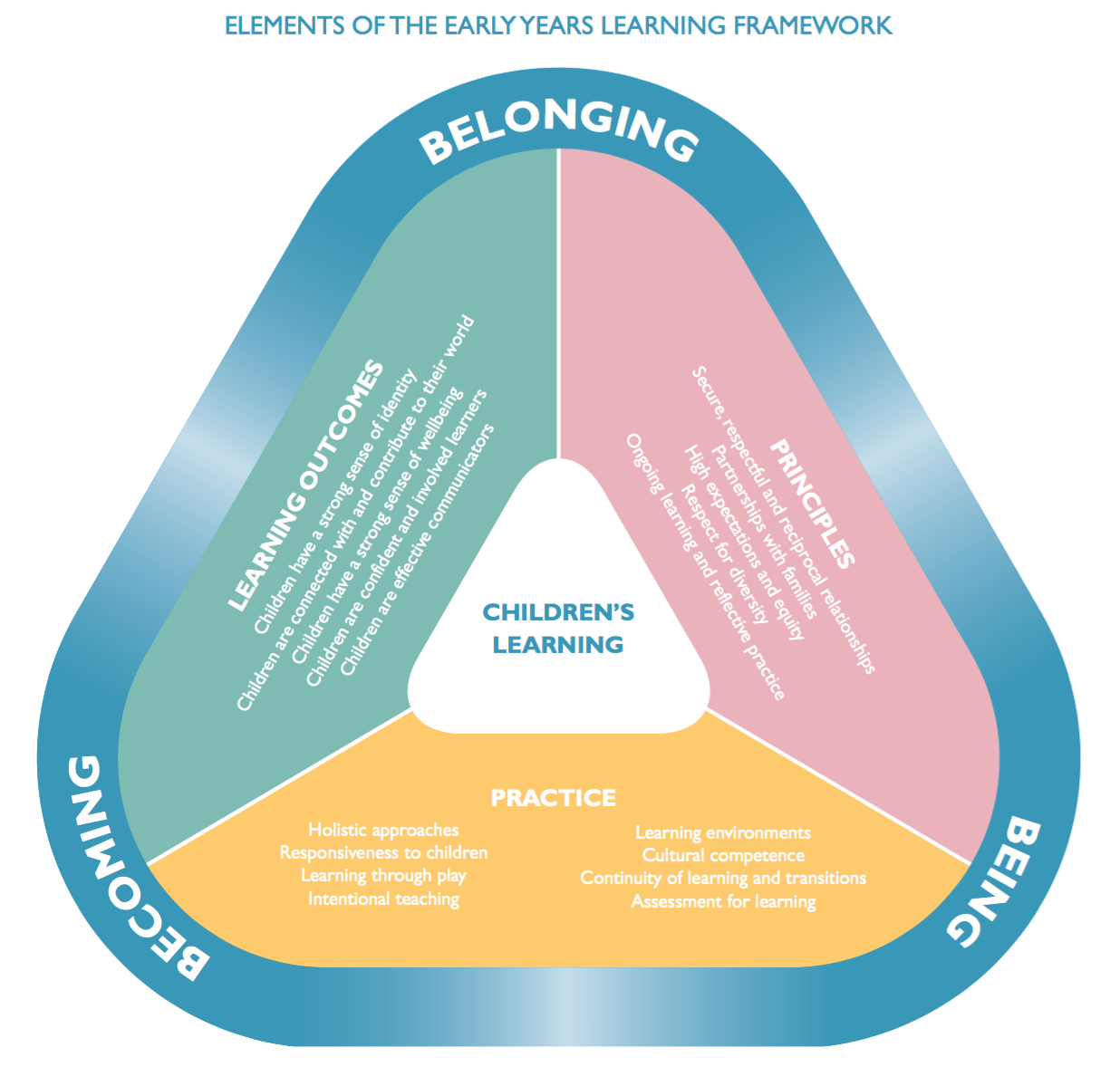
Early Years Learning Framework
The Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF) guides us to ensure your child’s progress through our babies, toddlers and preschool groups is linked to the learning outcomes found in the EYLF. This is reported on a daily, monthly and annual basis to the parents by means of emails and photos that are sent home daily and a beautiful annual portfolio of each child’s educational foundation years and resulting in school readiness.
“The Early Years Learning Framework is an early childhood curriculum framework, which will guide early childhood educators in developing quality, early childhood education programs. The framework describes the principles, practice and outcomes to support and enhance young children’s learning from birth to five years, as well as their transition to school. This will help ensure consistency in the delivery of learning programs around Australia.”
-mychild.gov.au